
Data quality is the lifeblood of good decision-making. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to missed opportunities, wasted resources, and even regulatory fines. But how do we ensure our data quality rules are effective?
- Conventional Data Quality Metrics
- Data Quality Rules are Business Rules
- Framing the Data Quality Conversation
- The Power of Business-Driven Rules
- Moving from Validation to Business Impact
Conventional Data Quality Metrics
Conventional data quality metrics like completeness rates (percentage of filled fields) and accuracy checks (validating formats) offer a quick snapshot of data health. They’re easy to implement and understand.
However, they often focus on technical aspects without considering the bigger picture. For example, a complete address field might still be useless if it lacks the correct post code for accurate delivery.
To ensure data truly serves business needs, a shift towards business-driven data quality rules is crucial.
Data Quality Rules are Business Rules
The secret lies in understanding that the best data quality rules are actually business rules. They go beyond simple validation checks and tie directly to the core objectives of your organization.
Let’s break down these business-driven data quality rules into three main categories:
1. Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
Many industries have strict regulations regarding data collection, storage, and usage. Data quality rules in this category ensure your data adheres to these regulations.
Example: Tax Invoices
In South Africa, there are specific legal requirements for invoices, especially tax invoices. These requirements include the name, address, and VAT registration number of the supplier, along with a serial number and the date of issue of the invoice. Additionally, there must be an accurate description of the goods or services provided, including their value, the amount of tax charged, and the consideration of the supply. For VAT invoices, if the recipient is a vendor, their name, address, and VAT identification must also be included.
Without these values invoices cannot be paid. By defining data quality rules that check these key fields for issues before issuing invoices a business can improve cash flow and speed up payments.
2. Enabling Business Operations/Processes
Accurate data is essential for smooth business operations. Data quality rules in this category ensure your data supports core business functions.
Example: Tax Invoices
Depending on the customer, your tax invoice may need to include a supplier ID number or a purchase order number amongst other values, or you may have contractually agreed discounts or payment terms. Errors in any of these fields may result in payment delays, customer complaints and other issues.
3. Enabling Key Reports
Data drives insights, and those insights come from reports. Data quality rules in this category ensure your data is reliable for generating accurate reports.
Example: Sales Performance Report
This report analyses sales data by product, customer, or salesperson. Inaccurate data on invoices, such as missing product codes or incorrect customer assignments, can lead to misleading insights into sales performance and hinder effective sales strategies.
Framing the Data Quality Conversation
Conventional data quality metrics and business rules can be powerful allies.
Metrics like completeness and accuracy can act as a starting point, identifying basic data issues. Business rules then take the reins, defining what “good” data truly means in your specific context. We suggest that business rules should also frame how data quality issues are presented.
For example, we can present the same issues in different ways as illustrated below:
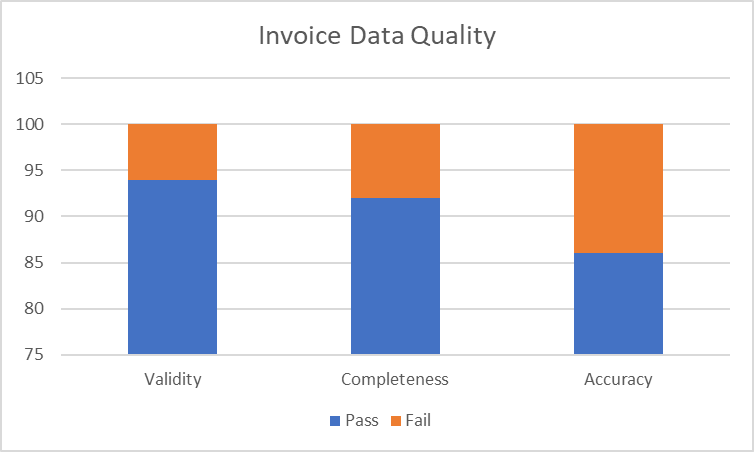
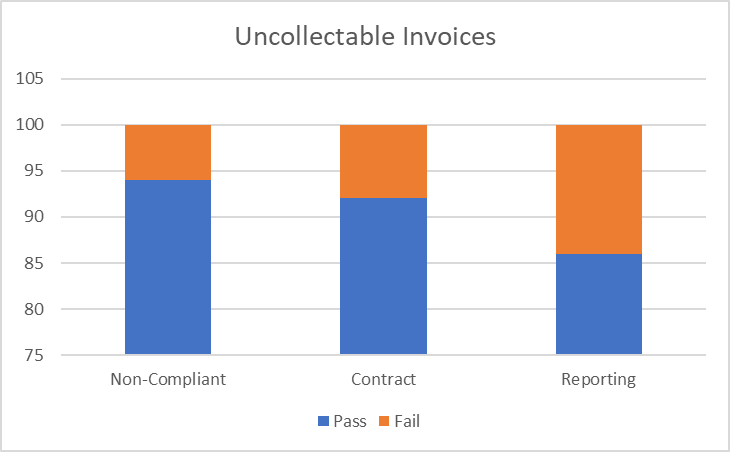

By combining metrics with business-driven rules, you get a holistic view of data quality, ensuring it meets not just technical standards, but also your unique business needs.
The Power of Business-Driven Rules
By framing data quality rules as business rules, you achieve several benefits:
- Alignment with Business Goals: Rules directly connect to business objectives, making them easier to understand and justify.
- Improved Stakeholder Buy-in: Business stakeholders see the value of data quality in achieving their goals, fostering collaboration.
- Prioritization and Focus: By aligning with business needs, you can prioritize which data quality rules have the biggest impact.
Moving from Validation to Business Impact
Here’s how to transform your data quality approach:
- Identify Business Needs: Start by understanding the core business objectives and processes that rely on data.
- Map Data Needs to Business Needs: Identify the specific data elements critical to those business needs.
- Define Data Quality Rules: Create clear and concise rules that ensure the accuracy, completeness, and consistency of these data elements.
By focusing on business-driven data quality rules, you move beyond simple validation and ensure your data is a strategic asset that drives informed decision-making and business success.


Leave a reply to Revue data du mois (avril 2024) – Datassence Cancel reply